Author’s Note: This is the original 8 Forms of Capital article from 2011. Our more recent book Regenerative Enterprise builds on the 8 Forms of Capital – you can download it at www.regenterprise.com, purchase a hardcopy, or get an ebook on Amazon.
For Ethan Roland Soloviev’s most up-to-date writing on regenerative agriculture, business, and life visit www.ethansoloviev.com
8 Forms of Capital
A whole system of economic understanding
©Copyright 2011 Ethan Roland & Gregory Landua
Context: Financial Permaculture, 2009
In 2008 and 2009, I was part of the organizing & facilitation team for the Financial Permaculture Course in Hohenwald, Tennessee. Convened by the Center for Holistic Ecology, Gaia University, and Solari, Inc, the course brought together permaculture designers, financial planners, entrepreneurs, community activists, complementary currency advocates, farmers and government officials from around the country.
Financial Permaculture goes beyond the traditional permaculture approach to economics and asks the question, “What would it look like if we re-designed the global financial system using permaculture principles?†and “What if our financial system looked more like an ecosystem?â€
In 2009, Catherine Austin Fitts presented “Mapping Financial Ecosystemsâ€. We mapped all the ‘capital pools’ in the local community. We explored the flows of money between entities, and discussed how vibrant local economies are more defined by the flows of money rather than by the pools. Something wasn’t sitting right with me. We kept talking about money as if it was the only form of capital, even though there was a growing awareness that acres of land, board feet of timber, and tons of carbon might also be part of an ecosystemic economy.
At one of the open space sessions I began to realize a more complete map of “capital.â€
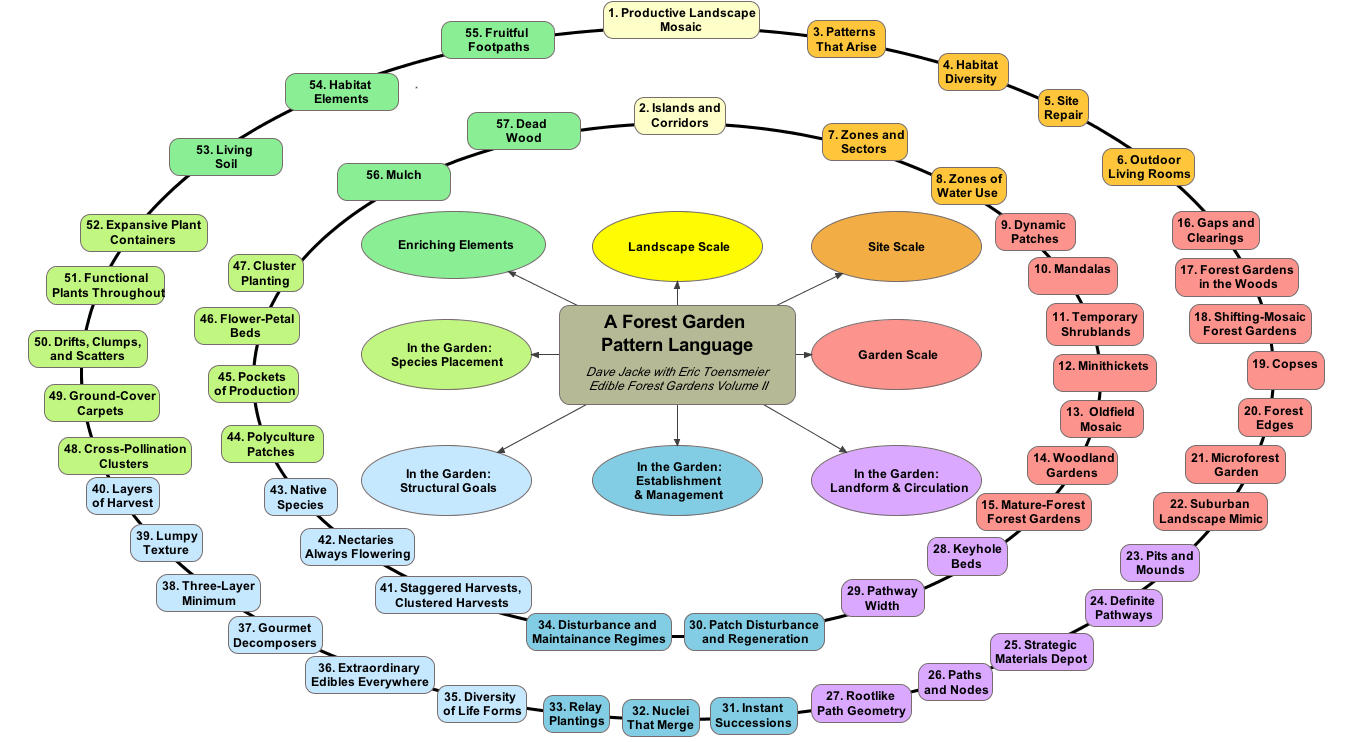
Eight Forms of Capital
The Oxford American Dictionary states that capital is, “wealth in the form of money or other assets†and a “valuable resource of a particular kind.†What are these ‘other assets’? I’ve never seen a whole map of all the different types of ‘valuable resources’. In the Permaculture Designers’ Manual, Bill Mollison offers and expands on a categorization of assets based on their potential: Degenerative, Generative, Procreative, Informational, Conservative (1). These always seem like a good way to think about things, but I don’t use them in any tangible way.
I wanted something that would be more helpful for understanding the complex transactions and exchanges swirling around me as a human being and us as a global community. As I considered the ‘mapping financial ecosystems’ exercise, a bigger picture began to emerge as I thought about the capital pools and flows of the Mayor of a hypothetical small town.
The Mayor might have some money (financial capital). A good Mayor would probably also have many friends in the town and some influence (social capital). The Mayor, who has a degree in economics, knows the stock market extremely well. S/he uses that intellectual capital to generate more money (financial capital) to run a re-election campaign, in which s/he works to transform financial capital into more social capital in the town.
I tried to enumerate all of the different ‘valuable resources’ which an individual or entity could gather or exchange. “Eight Forms of Capital†emerged:
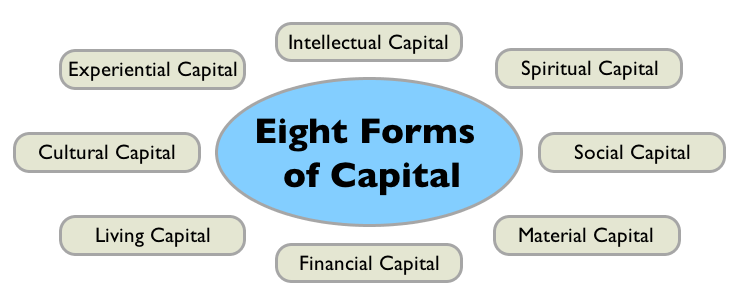
Social Capital
Influence and connections are social capital. A person or entity who has ‘good social capital’ can ask favors, influence decisions, and communicate efficiently. Social capital is of primary importance in politics, business, and community organizing.
Jason Eaton of Social Thread LLC explained to me that Capital can be in the form of equity or debt. In social capital, a person can ‘owe’ favors or decision-making influence to another person or entity.
Material Capital
Non-living physical objects form material capital. Raw and processed resources like stone, metal, timber, and fossil fuels are ‘complexed’ with each other to create more sophisticated materials or structures. Modern buildings, bridges, and other pieces of infrastructure along with tools, computers, and other technologies are complexed forms of material capital.
Financial Capital
We are most familiar with financial capital: Money, currencies, securities and other instruments of the global financial system. The current global society focuses enormous amounts of attention on financial capital. It is our primary tool for exchanging goods and services with other humans. It can be a powerful tool for oppression, or, (potentially) liberation.
Living Capital
A precious metal dealer who attended both Financial Permaculture courses advises, “Rather than U.S. Dollars, measure your wealth in ounces [of gold and silver]!†Recognizing that “precious†metals are just another form of financial capital, Catherine Austin Fitts recommends that we diversify and, “Measure your wealth in ounces, acres, and hooves.†Living capital is made up of the animals, plants, water and soil of our land— the true basis for life on our planet.
Permaculture design teaches us the principles and practices for rapid creation of living capital. Permaculture encourages us to share the abundance of living capital rather than the intangible “wealth†of financial capital.
(Note: “Natural Capital†could be a synonym for Living Capital, but the 1999 book “Natural Capitalism†by Hawkens et al. focuses more on a slightly updated system of capitalism than on the true wealth of living systems. The current Slow Money movement is also making strides in a similar direction, seeking to transfer financial capital into the living forms of soil, animals, and agriculture.)
Intellectual Capital
Intellectual capital is best described as a ‘knowledge’ asset. The majority of the current global education system is focused on imparting intellectual capital — whether or not it is the most useful form of capital for creating resilient and thriving communities. Having intellectual capital is touted as the surest way to ‘be successful’.Science and research can focus on obtaining intellectual capital or ‘truth’, though it is often motivated by the desire for financial or social capital. For example, “going to university†is primarily an exchange of financial capital for intellectual capital. It is supposed to prepare people for the rest of their lives in the world.
Experiential (or Human) Capital
We accumulate experiential capital through actually organizing a project in our community, or building a strawbale house, or completing a permaculture design. The most effective way to learn anything comes through a blended gathering of intellectual and experiential capital. My personal experience getting a Master’s degree at Gaia University showed me that experiential learning is essential for my effective functioning in the world: I was able to do projects instead of take classes, and I’m now collaboratively organizing the local permaculture guild and co-running a successful permaculture design firm (2).
I can see that ‘Human Capital’ is a combination of social, intellectual and experiential capital, all facets of a person that can be gathered and carried in essentially limitless amounts. But there’s one more form of capital that a person can gather and carry inside themselves.
Spiritual Capital
As one practices their religion, spirituality, or other means of connection to self and universe, one may accumulate spiritual capital. It contains aspects of intellectual and experiential capital, but is deeper, more personal and less quantifiable. Manyost of the world’s religions include a concept of ‘the great chain of being’, a holarchic understanding of existence where spiritual attainment (in this context, the accumulation of spiritual capital) leads to different levels of being (3).
Buddhism even contains an explicit spiritual currency: Karma! This form of spiritual capital is tallied and accounted for not only in one’s current life, but (taking re-incarnation into consideration) also in all of the past and future lives of one’s soul. In spiritual capital again enters the concept that capital can be in the form of equity (gathering positive spiritual experience/understanding/attainment) OR in the form of debt. In some Mayan cultures (like the Tzutujil of Lago Atitlan), a basic understanding of existence is that humans owe a ‘spiritual debt’ to the magnificent beauty and complexity of existence. According to this worldview, the goal of one’s life in the world is to create works of unspeakable beauty and gratitude, thereby repaying the spiritual debt to existence (4). The Tzutujil also recognize that single human beings can never really be effective at gathering and flowing capital if they are separated from their community.
Cultural Capital
All the other forms of capital may be held and owed by individuals, but cultural capital can only be gathered by a community of people. Cultural capital describes the shared internal and external processes of a community – the works of art and theater, the songs that every child learns, the ability to come together in celebration of the harvest or for a religious holiday. Cultural capital cannot be gathered by individuals alone. It could be viewed as an emergent property of the complex system of inter-capital exchanges that takes place in a village, a city, a bioregion, or nation.
Properties of the System
These eight forms of capital help us map our understanding of the world. The map clarifies that money is not the only form of capital flowing around and through us. This map expands the concepts of wealth (and poverty) to include the ‘valuable resources’ of personal connections, natural resources, land, knowledge, experience, and more. It provides a language for permaculture designers to communicate the value of healthy soil and healthy communities to people immersed in the current mindset of global capitalism, where financial capital is the only reality.
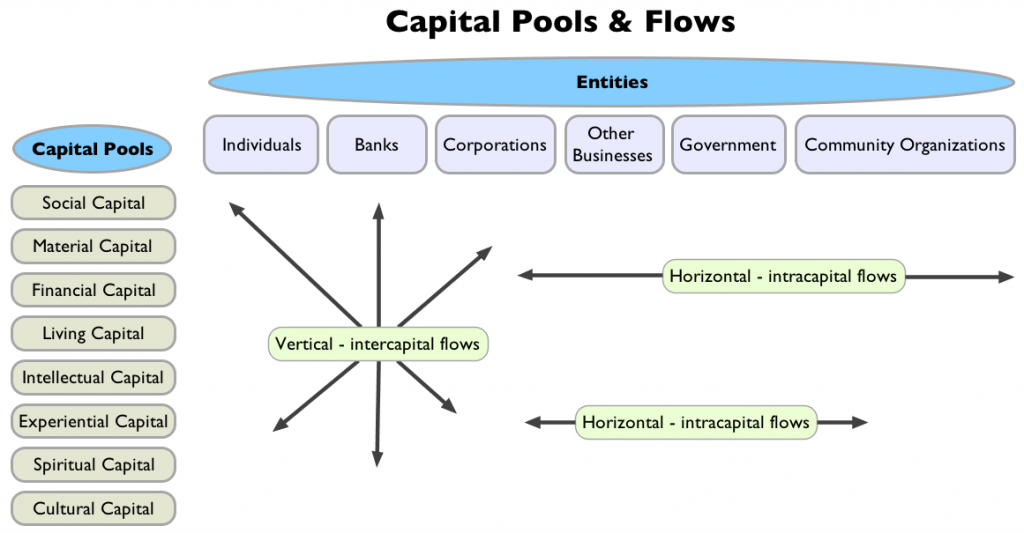
There are two types of flow between pools capital:
- Intra-capital flows, between the same type of capital. For example, using US dollars to purchase a stock or bond, or exchanging heirloom tomato seeds for a carton of eggs.
- Inter-capital flows, between different types of capital. For example, paying for a 2-year apprenticeship with a master builder would be an exchange of financial capital for experiential, intellectual, and even social capital.
These properties of capital flow point to another interesting question and feature of this map: What are the mediums of exchange used for each form of capital?
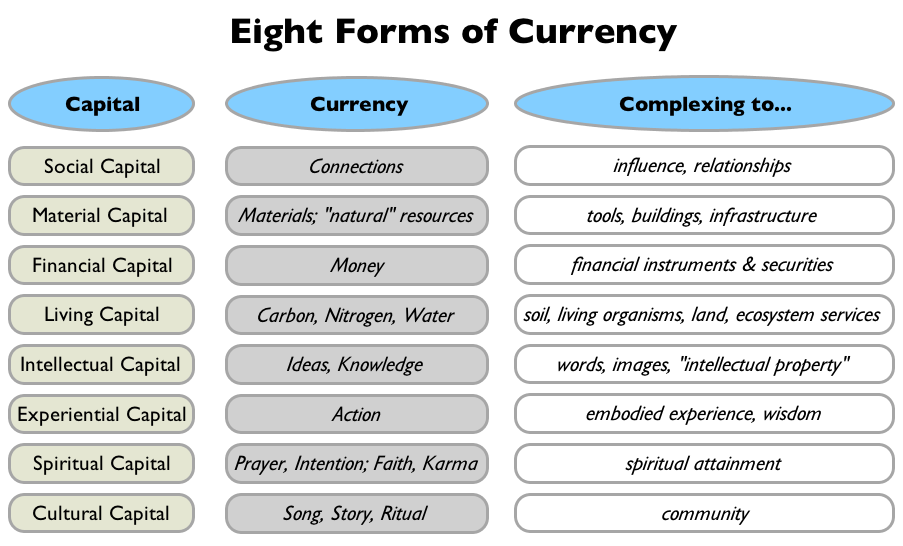
Eight Forms of Currency
Although most definitions of currency focus on financial capital, the Oxford American Dictionary and the Princeton Wordnet (5) both include the definition of “the fact or quality of being generally accepted or in useâ€. For this map, I define a currency as the generally accepted (or in use) medium of exchange between pools of capital. In many cases, the currency is the capital itself — for example, items of ‘Material Capital’ like copper or steel, can be the medium of exchange. Currencies can also be “complexed†into more interconnected and functional forms, and still used as a medium of exchange.
Here are the eight forms of currency associated with each form of capital:
Practical Applications
Earlier this year, as my partner and I designed a four-weekend series of Forest Garden courses, we were having a lot of trouble with the budget. The costs of renting space and paying teachers combined with our desire to keep fees affordable for the local community made the numbers look unfeasible. No matter how we changed things around, we couldn’t figure out how to make a reasonable financial return. Then we realized that our thinking was too narrow — we were only looking at financial capital! When we considered the experiential capital we’d gain by running a course, the social capital gathered by planting forest gardens at a new education center, and the living capital of hundreds of useful plants going into the ground… it became clear that financial remuneration was only one facet of the system. Nonetheless, we still needed to balance our inflow and outflow of this one form of capital.
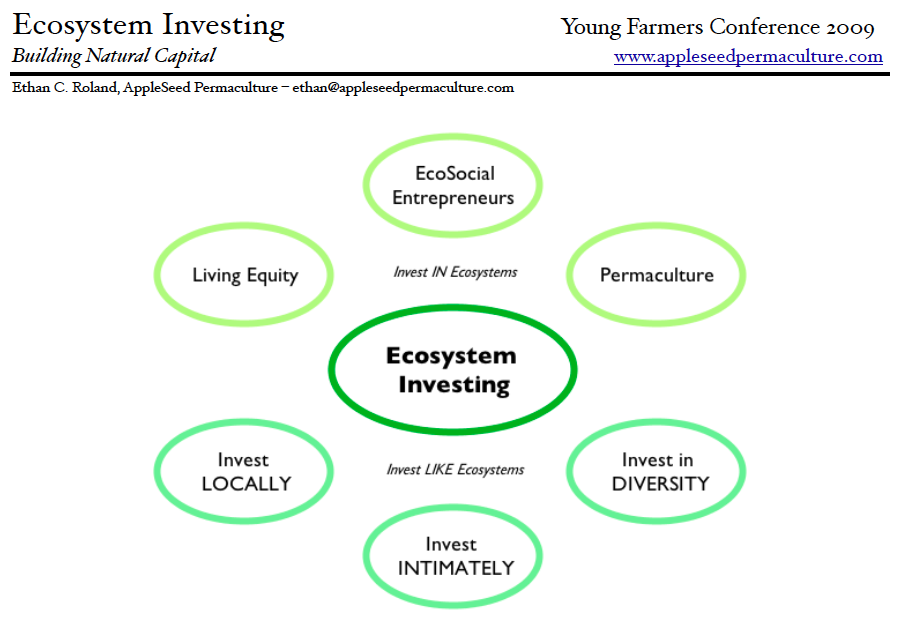
The eight forms of capital provide a clear path towards a small point of great leverage: Eco-social Investing. We can encourage individuals, businesses, organizations, and governments to mimic nature’s practices of investing: Locally, intimately, diversely, and primarily in living capital. The Financial Permaculture community, Gaia University, and a host of connected businesses and organizations are investing diverse baskets of capital, offering events like the Carbon Farming Course in Tennessee and the thriving eco-social chocolate business BooyaCacao.
I’ve outlined a set of principles for Eco-Social and Ecosystem Investing, which you can find on my blog at www.appleseedpermaculture.com/blog One of the most useful applications of this map is for growing and shifting our own understanding of the world and the transactions we engage in. When I volunteer time working on my friend’s organic permaculture farm, more than just ‘free labor’ is taking place:
- I’m gaining experiential and intellectual capital about the farm’s soil, crops, and management,
- We’re supporting the growth of healthy living capital in the soil,
- My friend gets help producing products to exchange for financial capital (her right livelihood)
- We both build social capital through positive interaction and connection with each other.
This amount of clarity can lead to a whole new level of transparency in our work as eco-social-cultural-economic designers. It can guide us towards an ever-deepening practice of the third ethic of permaculture.
The Third Ethic
Although Bill Mollison originally stated the third ethic of permaculture as “Setting limits to population and consumption,â€(6) many of us (especially in the more recent waves of permaculture) have been taught different forms of the third ethic. Some learn “Fair Share,†a toned-down and friendlier version of “Limitsâ€. Others learn “Resource Share,†which directs attention away from scarcity and towards re-investment of abundance. And more recently I’ve seen Starhawk refer to the third ethic as “Future Care,†which synthesizes the call for “Fair Share†and “Resource Share†into a focus on creating thriving inheritances for future generations. The eight forms of capital can and should be considered in terms of each version of the third ethic.
Fair Share
When people and the businesses, organizations, and governments understand the eight forms of capital, they may find that financial capital is not the whole system. This can lead to decreased consumption of non-essential goods and services that fuel our infinite-growth-based financial system.
A truly just society requires fair and equitable distribution of all forms of capital. While financial capital is important, non-financial capitals offer pathways to empowerment for the oppressed communities of our planet. In communities I’ve visited (Kazakhstan, Chile, and Latin America), the abundance of cultural capital often outweighs the financial capital, regenerating into a wealth of experiential and living capital that I’ve never seen in my northeastern-USA home. Any of us in the over-developed world can follow this modeling, working to end oppression caused by our current financial-capital-centric systems.
Resource Share
We can use the eight forms of capital to include resource sharing in our projects. AppleSeed Permaculture has set a new Carbon Policy, whereby 5% of our revenues will be dedicated to offsetting our carbon footprint through carbon-farming projects (living capital). The Permaculture Activist’s tree tax functions in much the same way, transforming financial capital into living capital for the good of the planet.
AppleSeed Permaculture is also inspired by our friends Shabazz and Josephine of Greenway Environmental Services, who explicitly donate 10% of every work week back to the community through education and consulting. They share their intellectual and experiential with urban youth groups and rural permaculturists alike, generating social capital for themselves at the same time. As an upper-middle class white male from the northeastern United States, I am seeking ways to transparently and joyfully use my multi-layered privilege to effectively share resources with those who have less power and freedom than I do. This article is one manifestation of my sharing of intellectual capital. I will also approach this goal through my work with eco-social investing. After seeking out leadership from people and communities who have been targeted by the oppressive effects of sexism, racism, and classism, their projects can be empowered through flows of multi-capital investment.
Future Care
To care for future generations, we need to move beyond finance into living and cultural capital. Of all eight forms, these two have the greatest potential for positive systemic change. Mollison writes, “We should develop or create wealth just as we develop landscapes, by conserving energy and natural resources [and] by developing procreative assets (proliferating forests, prairies, and life systems)â€(7). Only through the songs, stories, and shared ethics of cultural capital can a focus on living capital can be sustained for the seventh generation to come.
Some pieces are missing from the map: where does “labor†fit into the picture? What form of capital is “time� There may be some dangerous implications: this map could commodify ecosystem services, spirituality, and culture. To care for the future, we must think more holistically about our current capital system.
Let this map be a first draft. We don’t know what will happen in the future, but if a complex set of changes and capital flows appear along the way, I offer the eight forms of capital as a new map for the journey.
©Copyright 2011 Ethan Roland & Gregory Landua
Gratitude & Resources
I offer my deepest gratitude to Catherine Austin Fitts, Andrew Langford, Bill Mollison, Jason Eaton, Gregory Landua, Dyami-Nason Regan, Connor Stedman, Mai Frank, and Rafter Sass for their specific contributions to and reflections on this evolving map.
References
- Mollison, B. 1988. Permaculture: A Designers’ Manual p. 534. Tagari Publications, Tasmania, Australia.
- Roland, E. 2008. Gaia University Master’s Degree Portfolio, http://gel.gaiauniversity.org
- Wilber, K. 2001. A Theory of Everything: An Integral Vision for Business, Politics, Science, and Spirituality p. 66-69. Shambhala Publications, Massachusetts, United Staes
- Prechtel, M. 2009. Saving the Indigenous Soul: Derrick Jensen Interviews MartÃn Prechtel. Sun Magazine, December 2009
- Wordnet: A Lexical Database for English. http://wordnet.princeton.edu/, accessed 5/31/09.
- Mollison, B. 1988. Permaculture: A Designers’ Manual p. 2. Tagari Publications, Tasmania, Australia.
- Ibid. Permaculture: A Designers’ Manual p. 534. Tagari Publications, Tasmania, Australia.
Thanks for Reading! This is the original 8 Forms of Capital article from 2011. Our more recent book Regenerative Enterprise builds on the 8 Forms of Capital – you can download it at www.regenterprise.com, purchase a hardcopy, or get an ebook on Amazon.
For Ethan Roland Soloviev’s most up-to-date writing on regenerative agriculture, business, and life visit www.ethansoloviev.com

 Maintaining open space and farmland in our towns and cities provides many benefits. Recreational opportunities positively impact people’s emotional and physical health, while contact with trees and living systems has a profound impact on mental well-being. Children who spend more time in “green” settings have reduced symptoms of ADHD and higher test scores. The living systems provide numerous “ecosystem services” such as cleaning the air, infiltrating water and reducing runoff, cooling the community, and bolstering local biodiversity. The land base can also be utilized to grow food and other products to be consumed locally in a way that builds local economic resiliency and improves food security.
Maintaining open space and farmland in our towns and cities provides many benefits. Recreational opportunities positively impact people’s emotional and physical health, while contact with trees and living systems has a profound impact on mental well-being. Children who spend more time in “green” settings have reduced symptoms of ADHD and higher test scores. The living systems provide numerous “ecosystem services” such as cleaning the air, infiltrating water and reducing runoff, cooling the community, and bolstering local biodiversity. The land base can also be utilized to grow food and other products to be consumed locally in a way that builds local economic resiliency and improves food security.